1. Undang-undang.
Malaysia mempunyai kewajiban untuk memasukkan Regulasi Perserikatan Bangsa-Bangsa (United Nations Regulation) dalam Peraturan Legislasi Nasional Kendaraan Bermotor (Construction and Use) Rules 1959 dalam Undang-undang Transportasi Jalan 1987 (Road Transport Act 1987), sejak Malaysia masuk dalam World Forum for Harmonization of Vehicle Regulations (WP.29)
Road Transport Act 1987 Undang-undang ini diantaranya mengatur tentang klasifikasi kendaraan bermotor.
2. Kebijakan Pemerintah Malaysia.
National Automotive Policy Framework 2020.
Kebijakan Otomotif Nasional ini dipublikasi pada 21 Februari 2020, National Automotive Policy (NAP) 2020. Terdapat beberapa ketentuan dalam kebijakan ini, diantaranya langkah implementasi kebijakan, antara lain yang penting adalah:
- Memastikan kesesuaian standar dan kepatuhan teknis dengan melaksanakan Vehicle Type Approval (VTA) oleh Road Transport Department yang mengacu pada standar keamanan internasional, selain itu Department of Environment akan menegakkan standar emisi dan konsumsi bahan bakar. Penegakan standar wajib barang-barang manufaktur seperti itu akan mencegah impor produk di bawah standar.
- Mengurangi emisi karbon sejalan dengan ASEAN Fuel Economy Roadmap sebesar 5,3 Lge/100km pada tahun 2025.
3. Regulasi.
Pemerintah Malaysia melalui Kementerian Perhubungan masuk dalam World Forum for Harmonization of Vehicle Regulations (WP.29) sejak 4 April 2006. Melalui keanggotaan ini, Pemerintah Malaysia telah menandatangani Perjanjian, yaitu Perjanjian 1958 (Agreement concerning Adoption of Uniform Technical Prescriptions). Perjanjian 1958 adalah Perjanjian yang mewajibkan proses sertifikasi untuk setiap persetujuan standar teknis produk atau sistem otomotif.
3.1 Implementasi Regulasi Perserikatan Bangsa-Bangsa (PBB) di Malaysia.
Beberapa ketentuan yang diterapkan Malaysia dalam rangka implementasi Regulasi PBB.
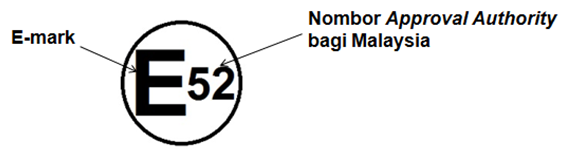
Sertifikasi E-Marking (E-Marking Certification).
Sertifikasi E-Marking adalah proses evaluasi, kepatuhan, pengujian dan sertifikasi yang dilakukan pada komponen otomotif dan sistem kendaraan bermotor berdasarkan regulasi PBB untuk memastikan keamanan kendaraan.
Sertifikasi E-Marking memungkinkan tanda ini digunakan dan ditempatkan pada setiap komponen oleh produsen atau pabrikan untuk menunjukkan bahwa komponen atau sistem tersebut mematuhi Regulasi PBB.
Contoh E-marking.

Kategori Kendaraan.
Berikut kategori kendaraan yang diterapkan.
- L: Motorcycle – Sepeda motor
- M1: Passanger Car – Mobil penumpang
- M2 dan M3: Bus/Coach – Bis/Bis wisata
- N1: Light Duty Truck/Lorry - Truk ringan
- N2 & N3: Heavy Duty Truck/Lorry – Truk berat
- O: Trailer/Semi-Trailer
Vehicle Type Approval Process (VTA).
Hingga saat ini, total 100 Regulasi PBB dari 136 Regulasi PBB telah ditetapkan ke dalam Motor Vehicle (Construction and Use) Rules 1959 (Aturan Kendaraan Bermotor (Konstruksi dan Penggunaan) 1959) yang dilaksanakan melalui the Vehicle Type Approval Process (VTA).
Semua kendaraan Kategori M, N, O, L, T serta komponen otomotif harus menjalani prosedur persetujuan jenis kendaraan sebelum diekspor ke pasar Malaysia.
Skema persetujuan Malaysia ditangani oleh lembaga berwenang (Jabatan Pengangkutan Jalan dan Department of Environment). Persetujuan sepenuhnya didasarkan pada persyaratan regulasi UNECE dan laporan / sertifikat pengujian UNECE diterima oleh pihak berwenang.
Component Type Approval (CTA).
Permohonan Persetujuan Jenis Komponen atau Component Type Approval (CTA) bertujuan untuk memastikan setiap komponen otomotif mematuhi standard wajib yang telah ditetapkan berikut.
|
No. |
Komponen |
Standar Wajib |
|
1. |
Topi Keledar |
R22 Protective Helmets and Their Visors for Driver and Passengers of Motorcycles and Moped |
|
Malaysia Standard (MS) 1: Protective Helmets for Vehicle Users |
||
|
2. |
Child Seat / Child Restraint System |
R44 Child Restraint Systems |
|
R129 Enhanced Child Restraint Systems (ECRS) |
||
|
3. |
New Brake Lining or Brake Pad |
R90 Replacement braking parts |
|
4. |
New Pneumatic Tyres & New Retreaded Pneumatic Tyres |
R54 Tyres for commercial vehicles and their trailers |
|
R108 Retreaded tyres for passenger cars and their trailers |
||
|
R109 Retreaded tyres for commercial vehicles and their trailers |
||
|
MS ISO 1394:2017 New pneumatic tyres for highway vehicles other than passenger cars – specifications (second revision) |
||
|
MS ISO 149:2018 New pneumatic passenger car tyres - specifications (third revision) |
||
|
MS ISO 224:2005 ,AMD. 1:2010 Retreaded pneumatic rubber tyres for passengger cars and commercial vehicles - specifications (second revision) |
||
|
5. |
Speed Monitoring Device |
R39 Speedometer |
|
6. |
Gas Discharge Headlamp / Bulb |
R98 Headlamps with gas-discharge light sources |
|
R99 Gas-discharge light sources |
||
|
MS ISO 303:2004 Installation of lighting and light signalling devices for motor vehicles and their trailers |
||
|
7. |
Seat |
R17 Strength of seats, their anchorages and head restraints |
|
R25 Head restraints (headrests) |
||
|
8. |
Safety Seatbelts |
R16 Safety-belts |
Lihat informasi tentang Component Type Approval berikut:
3.2 Prosedur Aplikasi Vehicle Type Approval (VTA).
Vehicle Type Approval (VTA) adalah prosedur yang dilakukan pada semua model kendaraan sebelum proses registrasi dilakukan. Hal ini dilakukan untuk menjaga identitas, dimensi, berat, karakteristik bangunan dan spesifikasi kendaraan untuk memastikan bahwa itu sesuai dengan ketentuan yang ditetapkan berdasarkan Undang-Undang Transportasi Jalan 1987 dan Aturan Transportasi Jalan.
Untuk memastikan prosedur dilakukan dengan lancar dan transparan, sebuah komite yang dikenal sebagai Komite Nasional untuk Persetujuan Tipe dan Homologasi dibentuk untuk menilai setiap aplikasi VTA untuk memastikan bahwa kendaraan mematuhi semua persyaratan.
Informasi selengkapnya, lihat Panduan VTA 2017.pdf
4. Standar.
Pengembangan standar / spesifikasi teknis kendaraan di Malaysia mengacu pada regulasi internasional melalui implementasi United Nation Economic Commission for Europe (UNECE).
4.1 Standar untuk Sertifikat Kendaraan Hemat Energi.
Departement of Standards Malaysia merilis Standar Malaysia "Energy efficient vehicle (EEV) - Requirements" (MS 2722:2021) yang menentukan persyaratan konsumsi bahan bakar untuk kendaraan hemat energi (EEV). Standar Malaysia ini dikembangkan dengan latar belakang perkembangan “National Automotive Policy 2020 (NAP 2020)”.
Standar Energy Efficient Vehicles: MS 2722:2021 Energy efficient vehicle (EEV) – Requirements specifies the requirements of motor vehicle fuel consumption for energy efficient vehicle
- Standar ini adalah standar sukarela dan tidak mengikat secara hukum.
- Lingkup Penggunaan. Kendaraan bermotor kategori (L, M and N) yang dikaslifikasikan pada standar MS 1822
- Label EEV. Otoritas yang kompeten di Malaysia mengeluarkan sertifikat EEV. Dan, kendaraan yang disetujui sebagai EEV oleh otoritas yang berwenang dapat ditandai dengan label EEV seperti contoh berikut.
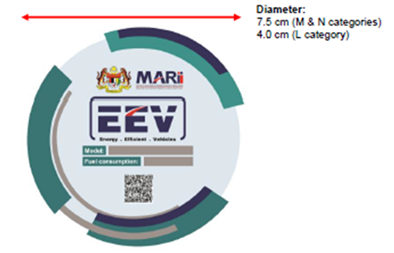
- Standar sertifikasi EEV. Sebagai contoh, batas konsumsi bahan bakar EEV berdasarkan bobot bersih ditunjukkan pada tabel berikut.
|
Kerb Weight (kg) |
Fuel Consumption Limits (L/100km) |
|
<800 |
4.5 |
|
801-1000 |
5.0 |
|
1001-1250 |
6.0 |
|
1251-1400 |
6.5 |
|
1401-1550 |
7.0 |
|
1551-1800 |
9.5 |
|
1801-2050 |
11.0 |
|
2051-2350 |
11.5 |
|
2351-2500 |
12.0 |
|
2501-2750 |
13.5 |
|
2751-3000 |
14.7 |
|
3001-3250 |
16.0 |
|
3251-3500 |
17.2 |
4.2 Standar Suku Cadang Otomotif.
Beberapa standar yang diterapkan untuk suku cadang otomotif.
Seat Belt:
- MS 1175:2003 Specification for Seat Belts for Motor Vehicles (First Revision).
- MS 1175:2003 (CONFIRMED:2016) Specification for seat belts for motor vehicles (Second revision) specifies the safety belts and restraint systems which are designed for installation in vehicles and are intended for separate use.
- MS 1154:2003 (CONFIRMED: 2016) Specification for webbing for car seat belts (First revision) applies to webbing used in the construction of automotive seat belts, which depends on the properties of the webbing.
- MS 75:2002 (CONFIRMED: 2016) Specification for anchorages for seat belts (First revision) specifies basic requirements for the locations and testing of anchorages for seat belts in motor vehicles.
Clutch and Brakes.
- MS 2585:2014 Road vehicles - clutches and brakes - Vocabulary specifies the fundamental terms and definitions of the clutches and brakes for road vehicles.
- MS 2585:2014, ERR. 1:2015 Road Vehicles - clutches and brakes - Vocabulary ERRATA 1 specifies the fundamental terms and definitions of the clutches and brakes for road vehicles.
- MS 474: PART 2:2003 Methods of Test For Automotive Friction Materials (Brake Linings, Disc Pads and Bonded Shoe): Part 2: Rockwell Hardness Test (First Revision) specifies the method of Rockwell hardness test for drum brakelining, disc brake pads and clutch facing of automobiles.
- MS 474-2:2003 (CONFIRMED:2016) Methods of test for automotive friction materials (Brake linings, disc pads and bonded shoe): Part 2: Rockwell hardness test (First revision) specifies the method of Rockwell hardness test for drum brake lining, disc brake pads and clutch facing of automobiles.
- MS ISO 6312:2011 Brake pad and drum brake shoe assemblies (First revision) (ISO 6312:2010, IDT) specifies a method for measuring the strength of the bond connection between the lining material and the carrier in disc brake pad and drum brake shoe assemblies (shear strengt h).
- MS ISO 4930:2008 (CONFIRMED: 2013) Brake cylinders using a non-petroleum base hydraulic brake fluid (Service temperature 150 °C max.) (ISO 4930:2006, IDT) specifies the performance test methods and requirements for elastomeric seals used in road vehicle disc brake cylinders.
- MS 2082:2008 (CONFIRMED:2013) Road vehicles - Braking systems - Temperature measuring methods presents methods for measuring the temperature of braking systems in road vehicles. It is applicable to both disc and drum brake s fitted for passenger cars and commercial vehicles, and its methods are suitable for either dynamometer tests in the laboratory or vehicle tests on road and track.
- MS 2046:2008 (CONFIRMED:2013) Road vehicles - Brake linings frictions materials - Visual inspection defines visual aspect for the identification and assessment of such product characteristics in quality assurance, as well as a basis for commercial and technical agreements.
Glazing and Film.
- MS 595-1:2022 Specification for safety glazing materials for motor vehicles - Part 1: General requirements (Third revision).
- MS 595-2:2022 Specification for safety glazing materials for motor vehicles - Part 2: Methods of test (Third revision).
- MS 2669:2017 Tint film on glazing of road vehicles - Methods and requirements of light transmittance, ultraviolet transmittance, total solar energy transmittance and other related factors specifies methods and requirements of visible light, energy transmittance of solar radiation and other related factors for tint film on the glazing in road vehicles. It covers the specification and requirement of visible light transmittance, ultraviolet transmittance, total solar energy transmittance and other performance of tint film.
- MS 2669:2017, AMD. 1:2018 Tint film on glazing of road vehicles - Methods and requirements of light transmittance, ultraviolet transmittance, total solar energy transmittance and other related factors specifies methods and requirements of visible light, energy transmittance of solar radiation and other related factors for tint film on the glazing in road vehicles. It covers the specification and requirement of visible light transmittance, ultraviolet transmittance, total solar energy transmittance and other performance of tint film.
Vehicle Security System.
- MS 1742-1:2004 (CONFIRMED:2013) Vehicle security systems: Part 1: Guidelines to the application of security systems to vehicles is intended to provide information and guidance on the various types of security devices and systems that are available, the range of protection devices and systems.
- MS 1742-2-1:2004 (CONFIRMED:2013) Vehicle security systems: Part 2: Locking systems: Section 1: Specification for locking systems specifies requirements for the performance of locking systems fitted to passenger compartment doors and luggage compartment or hatchbacks doors of passenger cars.
- MS 1742-2-2:2004 (CONFIRMED:2013) Vehicle security systems: Part 2: Locking systems: Section 2: Specification for central power locking systems specifies requirements for the performance of central locking systems fitted to passenger compartment doors and luggage compartment or hatchbacks doors of passenger cars.
- MS 1742-2-3:2004 (CONFIRMED:2013) Vehicle security systems: Part 2: Locking systems: Section 3: Specification for dead locking systems specifies requirements for the performance of dead locking systems fitted to passenger compartment doors, luggage compartment or hatchback doors, engine compartment access.
- MS 1742-2-4:2005 (CONFIRMED:2013) Vehicle security systems - Part 2: Locking systems - Section 4: Specification for devices for prevention against unauthorised use specifies requirements for the devices designed to prevent unauthorised use of M1 and N1 vehicles. This standard does not cover the requirements for immobilizer.
- MS 1742-3:2004 (CONFIRMED:2013) Vehicle security systems: Part 3: Specification for alarm systems specifies requirements and test methods for vehicle security alarm systems (VSAS) intended as original equipment and for post delivery installation on M1 vehicle
- MS 1742: PART 4:2004 Vehicle Security Systems: Part 4: Specification for Immobilizer specifies requirements for the performance of vehicle security immobilizer systems (VSIS) in road vehicles such as private cars, and commercial and heavy goods vehicles.
Belt and Pulley.
- MS ISO 5287:2009 (CONFIRMED:2020) Belt drives - Narrow V-belts for the automotive industry - Fatigue test (ISO 5287:2003, IDT) specifies a fatigue test for the quality control of narrow V-belts (sections AV 10 and AV 13) intended for driving the auxiliaries of internal combustion engines
- MS ISO 2425:2011 (CONFIRMED:2016) Belt drives - V-belts for the automotive industry and corresponding pulleys - Dimensions specifies the following items with regard to V-belts (hereafter referred to as belts) and V-pulleys (hereafter referred to as pulleys) used to drive auxiliary parts
- MS ISO 9981:2010 (CONFIRMED: 2016) Belt drives - Pulleys and V-ribbed belts for the automotive industry - PK profile: Dimensions (ISO 9981:1998, IDT). The adoption of the ISO Standard as a Malaysian Standard was recommended by the Technical Committee on Vehicle Powertrain and Fuels Systems under the authority of the Industry Standards Committee on Road Vehicles.
- MS ISO 9010:2010 Synchronous Belt Drives - Automotive Belts (ISO 9010:1997, IDT). The adoption of the ISO Standard as a Malaysian Standard was recommended by the Technical Committee on Vehicle Powertrain and Fuels Systems under the authority of the Industry Standards Committee on Road Vehicles.
- MS ISO 9011:2010 Synchronous Belt Drives - Automotive Pulleys (ISO 9011:1997, IDT). The adoption of the ISO Standard as a Malaysian Standard was recommended by the Technical Committee on Vehicle Powertrain and Fuels Systems under the authority of the Industry Standards Committee on Road Vehicles.
Suspension.
- MS 2613:2017 Road vehicles - Suspension strut and telescopic shock absorbers strength and durability specifies the strength and durability requirements for suspension strut and telescopic shock absorbers of M1 and N1 categories.
- MS 2321:2010 (CONFIRMED:2016) Road vehicles - Telescopic sock absorbers for suspension systems specifies telescopic shock absorbers used for automobile suspensions systems (herein referred to as shock absorber).
- MS 1916:2006 Road Vehicles – Suspension Struts for Automobiles specifies the strut bodies of the suspension struts for automobiles.
- MS 1108:1988 Specification for Suspension Coil Springs for Automotive Use specifies Material, dimension and performance requirements for cylindrical coil compression springs made from round bars for use in the suspension system of motor vehicles. The coil spring serves as a suspension spring between the chassis and the body. It shall be located between two spring seats which have been adopted to suit the design of the ends of the spring.
- ·MS ISO 611:2005 (CONFIRMED:2011) Road Vehicles - Braking of Automotive Vehicles and Their Trailers - Vocabulary (ISO 611:2003, IDT) was developed by the Technical Committee on Braking System, Suspension and Mechanical Support under the authority of the Road Vehicles Industry
Komponen Lainnya.
- MS IEC 60810:2008 lamps for Road Vehicles – Performance Requirements (First Revision) (IEC 60810:2003, IDT) is applicable to replaceable lamps (filament lamps and discharge lamps) to be used in headlamps, fog-lamps and signalling lamps.
- MS ISO 13476:2009 (CONFIRMED:2016) Road Vehicles - Ignition Coils - Electrical Characteristics and Test Methods (ISO 13476:1997, COR. 1:1999, IDT) applies to ignition coils for inductive energy storage. It defines test methods for ignition coils used in ignition systems with solid state switching of spark ignited internal combustion engines.
- MS 2328-1:2010 Ergonomics of The Thermal Environment - Evaluation of Thermal Environments in Vehicles - Part 1: Principles and Methods for Assessment of Thermal Stress
- MS ISO 14505-2:2008 Ergonomics of The Thermal Environment - Evaluation Of Thermal Environments in Vehicles - Part 2: Determination of Equivalent Temperature (ISO 14505-2:2006, LDT)
- MS ISO 14505-3:2008 Ergonomics of the Thermal Environment - Evaluation of Thermal Environments in Vehicles - Part 3: Evaluation of Thermal Comfort Using Human Subjects (ISO 14505-3:2006, IDT)
- MS ISO 11154-1:2005 Road Vehicles - Roof Load Carriers - Part 1: Roof Bars (ISO 11154-1:1995, LDT) specifies the minimum safety requirements for roof bars intended for mounting on or above the roofs of passenger cars or light commercial vehicles with a maximum authorized total mass (ISO-M08) as defined in IS0 1176 up to 3.5 t.
- MS ISO 10604:2006 Road Vehicles – Measurement Equipment for Orientation of Headlamp Luminous Beams (ISO 10604:1993, IDT) The adoption of the ISO Standard as a Malaysian Standard was recommended by the Technical Committee on Lighting and Signalling under the authority of the Road Vehicles Industry Standards Committee.
- MS ISO 10455:2005 (CONFIRMED: 2012) Road vehicles- Dry ignition coils using rotating high-voltage distributor (ISO 10455:1992, IDT). This Malaysian Standard was developed by the Technical Committee on Electrical and Electronic Equipment under the authority of the Road Vehicles Industry Standards Committee.
- MS ISO 10392: 2008 Road Vehicles with Two Axles - Determination of Centre Of Gravity (ISO 10392:1992, IDT). The adoption of the ISO Standard as a Malaysian Standard was recommended by the Working Group on Construction of Vehicles under the authority of the Industry Standards Committee on Road Vehicles.
- MS ISO 8854: 2009 Road Vehicles - Alternators with Regulators - Test Methods and General Requirements (First Revision) (ISO 8854:1988, IDT). The adoption of the ISO Standard as a Malaysian Standard was recommended by the Technical Committee on Electrical and Electronic Equipment under the authority of the Industry Standards Committee on Ro ad Vehicles.
- MS ISO 6518-1: 2005 (CONFIRMED: 2016) Road vehicles - Ignition systems: Part 1: Vocabulary (ISO 6518-1:2002, IDT) defines terms related to the ignition systems of spark-ignited internal combustion engines intended for use in road vehicles.
- MS ISO 4020:2005 (CONFIRMED: 2016) Road vehicles - Fuel filters for diesel engines - Test methods specifies the types of test for fuel filters in accordance with their application. This standard applies to fuel filters provided for road vehicles with diesel engines and for test installations for fuel injection equipment.
- MS ISO 3553-1:2005 Road Vehicles - High-Tension Connections for Ignition Coils and Distributors - Part 1: Socket-Type (ISO 3553-1:1987, IDT) specifies the essential dimensions of high-tension socket -type connections for ignition coils and distributors, used for spark-ignition engines. This standard applies to high-tension sockets and to high-tension cable connectors of type “A”.
- MS ISO 3553-2:2005 Road Vehicles - High-Tension Connections for Ignition Coils and Distributors - Part 2: Plug Types (ISO 3553-2:1997, IDT) specifies the essential dimensions of plug-type high-tension connectors for ignition coils and distributors, used for spark-ignited engines.
- ·MS 2413:2022 - Electric motorcycles - Specification (First revision) specifies the general specification of electric motorcycles for on-the-road use.
- MS 2730:2021 Next Generation vehicle (NxGV) – Terminology, definition and levels of Autonomous, Automated and Connected vehicle (AACV)
Lihat selengkapnya disini.
5. Lembaga Berwenang.
Department of Standards Malaysia – Ministry of Investment, Trade and Industry (MITI)
Level 4-7, Tower 2, Menara Cyber Axis
Jalan Impact, Cyber 6
63000 Cyberjaya
Selangor, MALAYSIA
Tel: +603-8008 2900
Fax: +603-8008 2901
Department of Environment, - Ministry of Natural Resources, Environment and Climate Change
Level 1 – 4, Podium 2 & 3, Wisma Sumber Asli No.25, Persiaran Perdana, Precinct 4,
Federal Government Administrative Centre,
62574 Putrajaya, Malaysia.
Jabatan Pengangkutan Jalan
Aras 3-5, No. 26,
Jalan Tun Hussien, Presint 4,
Pusat Pentadbiran Kerajaan Persekutuan,
62100 WP Putrajaya
6. Informasi Lainnya.
- Malaysia’s National Automotive Policy 2020: Salient Features
- Implementaion of United Nations (UN) Regulations in Malaysia